Few automotive brands command the same level of prestige and admiration as Mercedes-Benz. Known worldwide for its luxury, innovation, and performance, Mercedes-Benz has been a pioneer in the automotive industry for nearly a century. From its iconic three-pointed star emblem to its cutting-edge engineering, the brand represents excellence and sophistication. But who owns Mercedes-Benz, and where are its world-renowned vehicles manufactured? Let’s explore the brand’s rich history, ownership structure, and global production network.
A Legacy of Innovation: The History of Mercedes-Benz
The origins of Mercedes-Benz trace back to 1926, when Karl Benz, Gottlieb Daimler, Wilhelm Maybach, and Emil Jellinek joined forces to create the company. However, its roots go even deeper. In 1886, Karl Benz invented the Patent Motorwagen, widely recognized as the world’s first gasoline-powered car. Around the same time, Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach were developing their own revolutionary engines.
The name “Mercedes” was trademarked by Emil Jellinek in honor of his daughter, Mercedes Jellinek. Jellinek, a forward-thinking entrepreneur, marketed these early vehicles to the elite, including billionaires like John Jacob Astor and J.P. Morgan, solidifying the brand’s reputation as a symbol of luxury and success.
In 1926, Benz & Cie. and Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG) merged to form Mercedes-Benz. The iconic three-pointed star emblem, introduced in 1909, became the brand’s official logo after the merger. Over the decades, Mercedes-Benz has led the way in automotive innovation, introducing groundbreaking technologies such as the first fully independent suspension (1931), the Anti-lock Braking System (1978), and advanced features like Car-to-X Communication.
Who Owns Mercedes-Benz Today?
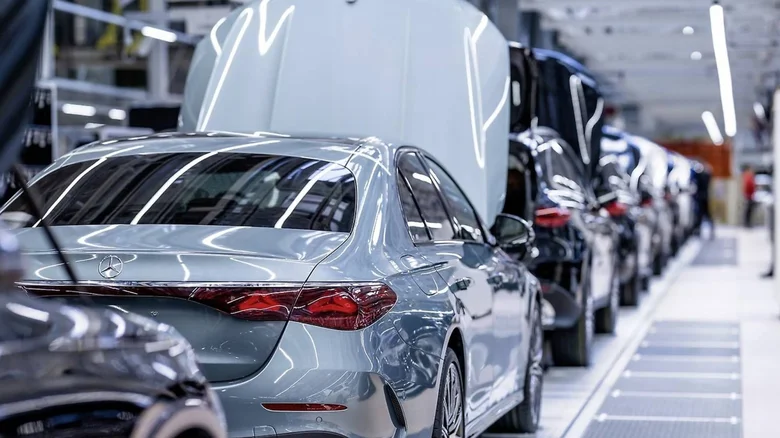

Mercedes-Benz operates under Mercedes-Benz Group AG, a publicly traded company headquartered in Stuttgart, Germany. Formerly known as Daimler AG, the company rebranded in 2022 to emphasize its focus on luxury vehicles and electric mobility.
As a publicly traded entity, Mercedes-Benz Group AG has nearly 1 billion shares distributed worldwide. Its ownership structure includes several key stakeholders:
BAIC Group: The Chinese automotive conglomerate holds a 9.98% stake, making it the largest shareholder.
Li Shufu (Geely): The founder of Geely, a Chinese automaker, owns a 9.69% stake through Tenaciou3 Prospect Investment Limited.
Kuwait Investment Authority: A long-term investor, the Kuwaiti sovereign wealth fund has held shares in the company since 1974.
While these international entities hold significant stakes, Mercedes-Benz remains deeply rooted in its German heritage, with its headquarters and primary operations centered in Stuttgart.
Where Are Mercedes-Benz Cars Made?
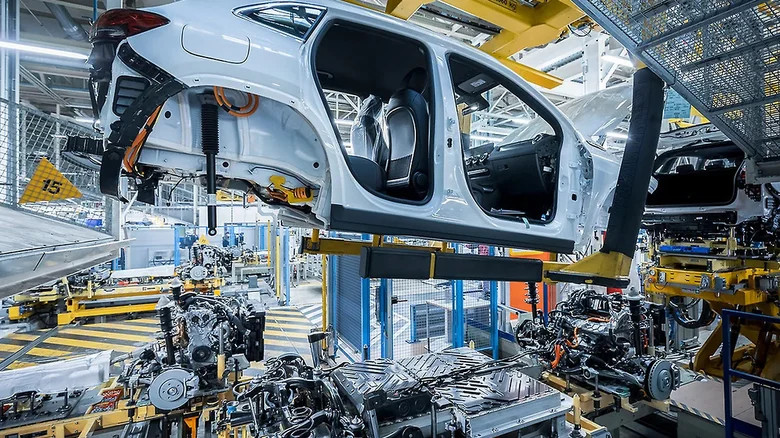

Mercedes-Benz operates a global manufacturing network, with production facilities strategically located across five continents. Each plant specializes in specific models, ensuring the highest standards of quality and efficiency. Here’s a look at some of the brand’s key production sites:
Germany: The Heart of Mercedes-Benz Production
Bremen Plant: Operational since 1978, this facility has produced over 10 million vehicles, including the C-Class, GLC, and electric models like the EQE. It also manufactures high-performance AMG models such as the SL roadster and AMG GT.
Sindelfingen Plant: One of the oldest and most advanced facilities, dating back to 1915, it produces luxury models like the E-Class, S-Class, Maybach S-Class, and the all-electric EQS. The plant is home to Factory 56, a state-of-the-art assembly hall that sets new standards in automotive manufacturing.
Rastatt Plant: Since 1992, this facility has focused on compact models, including the A-Class, B-Class, GLA, and the electric EQA.
United States: A Hub for SUVs and Luxury Models
Tuscaloosa, Alabama: Since 1995, this plant has produced SUVs like the GLE and GLS, as well as the ultra-luxurious Maybach GLS. In 2022, it expanded to include electric SUVs such as the EQS and EQE.
China: Catering to the World’s Largest Automotive Market
Beijing Benz Automotive Co. (BBAC): A joint venture with BAIC Motor, this facility has been producing Mercedes-Benz vehicles since 2005. It specializes in extended-wheelbase versions of the C-Class, E-Class, and GLC, as well as electric models like the EQA, EQB, and EQE.
Hungary: Compact Models and Electric Vehicles
Kecskemet Plant: Opened in 2021, this facility produces compact models like the A-Class, CLA Coupe, and the entry-level EQB electric SUV. It is unique for assembling vehicles with combustion engines, plug-in hybrids, and fully electric drivetrains on the same production line.
South Africa: Supporting Global Demand
East London Plant: Since 2021, this facility has played a crucial role in the global supply chain by producing C-Class sedans for both left- and right-hand drive markets.
Mercedes-Benz’s Commitment to Innovation and Sustainability
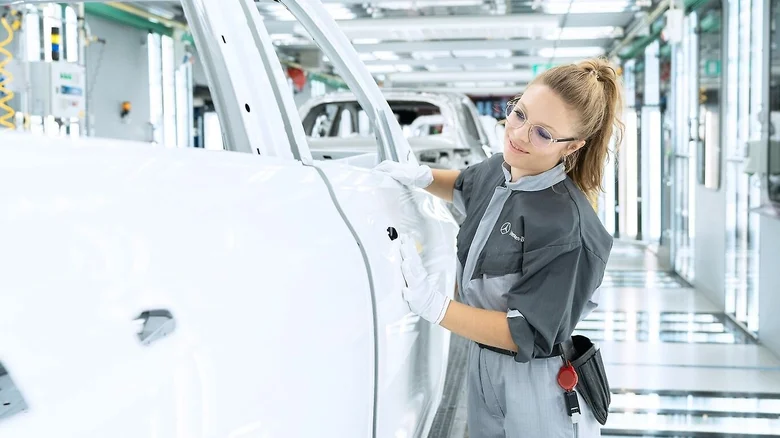

Mercedes-Benz is not just a leader in luxury and performance; it is also at the forefront of sustainability and innovation. The company has set ambitious goals to achieve carbon neutrality across its production network by 2039. Its investments in electric mobility, such as the EQ lineup, and advanced manufacturing technologies like Factory 56, demonstrate its commitment to shaping the future of the automotive industry.
Mercedes-Benz is more than just a car manufacturer; it is a symbol of excellence, innovation, and luxury. With a rich history dating back to the invention of the automobile, the brand continues to push boundaries under the ownership of Mercedes-Benz Group AG. Its global production network, spanning Germany, the United States, China, Hungary, and South Africa, ensures that every vehicle meets the highest standards of quality and craftsmanship.
Whether you’re driving a sleek C-Class sedan, a powerful AMG GT, or an eco-friendly EQE, you’re experiencing the legacy of a brand that has defined automotive excellence for over a century. As Mercedes-Benz embraces the future of electric mobility and sustainable manufacturing, its commitment to innovation and luxury remains unwavering.