A few weeks ago, I tested how the Nvidia RTX 5090 Founders Edition, one of the most advanced GPUs, performed inside a compact small form factor (SFF) PC. Surprisingly, it retained much of its power, even in a 12.7-liter desktop with an older processor. That sparked an idea: what if I connected this GPU to a handheld gaming PC?
So, I gave it a shot—and the results were truly remarkable.
This experiment challenges the traditional notion of handheld gaming. If portable devices can leverage such power when docked, they could potentially evolve into high-performance gaming systems at home.
The Setup: Maximizing Power in a Portable Device
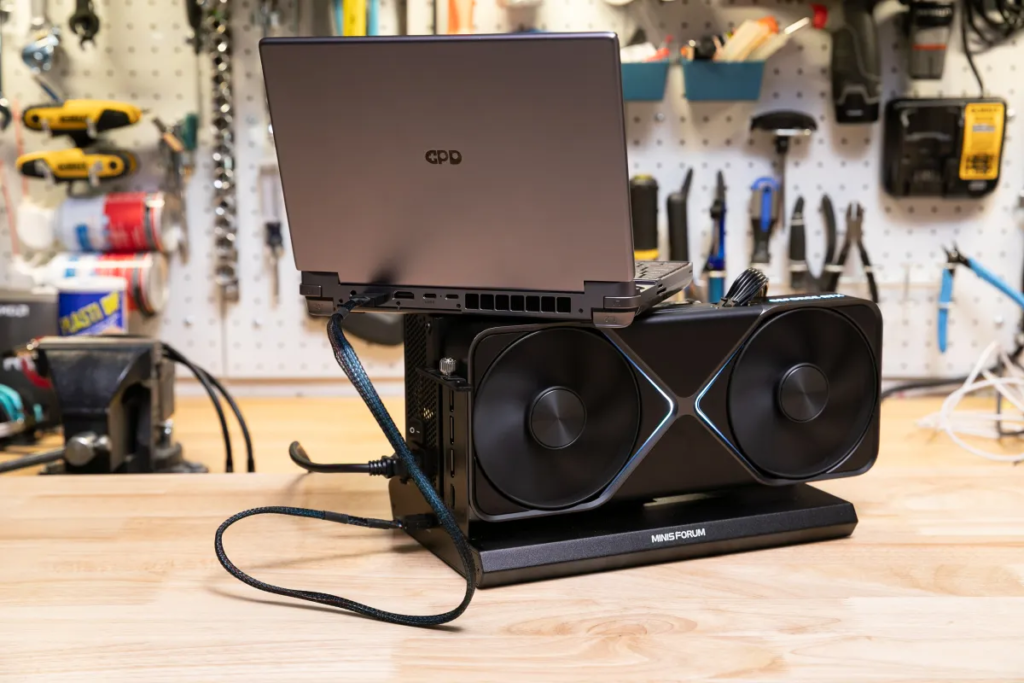

For this test, I used the same $1,999 RTX 5090 Founders Edition along with a 1000-watt power supply from my earlier SFF desktop trial. A key component was the $99 Minisforum DEG1, an open-air external GPU (eGPU) dock that connects via Oculink, a high-speed PCIe-based interface now appearing in select handheld gaming systems.
For the handheld, I chose the $1,000 GPD Win Max 2, powered by an AMD Ryzen 8840U mobile CPU. Even though it only supports four lanes of PCIe 4.0 bandwidth, significantly less than the 16 lanes of PCIe 5.0 that the RTX 5090 is designed for, the performance was still impressive.
Performance Insights: Defying Expectations
Despite the limited PCIe bandwidth, the setup achieved over 100 FPS in Cyberpunk 2077 at 4K Ultra settings, a remarkable achievement for a portable system. The results across eight benchmarked games were eye-opening:

The RTX 5090 in the GPD Win Max 2 ran 7–47% slower than when paired with the most powerful desktop gaming CPU.
Compared to my SFF desktop, performance was reduced by only 4–29%, despite the bandwidth limitations.

It still outperformed an RTX 3080 in the SFF desktop, showcasing that even under constraints, the RTX 5090 delivers exceptional performance.
Most impressively, it was 4–12 times faster than the handheld’s Radeon 780M integrated GPU.
The Future of Handheld Gaming
This experiment is more than just a technical exercise—it highlights the potential for handheld gaming. Here are the key takeaways:
Docked Gaming Will Elevate Handheld Devices – With the growing adoption of Oculink and eGPU technology, portable gaming systems can remain compact while achieving desktop-class performance when docked.
External GPUs May Become a Standard Accessory – If high-speed PCIe interfaces like Oculink continue to gain traction, we could see plug-and-play eGPU docks becoming a common feature for handheld gaming PCs.
Handhelds Could Become More Modular and Upgradable – Optimizing bandwidth and power efficiency could lead to future handhelds that effectively bridge the gap between portability and high-end gaming performance.
While running an RTX 5090 on a handheld device isn’t practical for everyday gaming, this experiment proves an important point: the line between handheld and desktop gaming is becoming increasingly blurred.
If companies like Nvidia, AMD, and handheld PC manufacturers continue to push these boundaries, the future of mobile gaming could be more powerful than we ever imagined.