BMW has built a reputation for producing high-performance engines, from its iconic inline-four-cylinder engines, such as the 2.3-liter found in the E30 M3, to the elite V12s that powered a select few coveted models. Alongside these petrol engines, BMW has also created some of the most powerful and reliable diesel engines in the industry, including the famous M57, which had a production span of 13 years and came in multiple variants.
In this post, we take a closer look at the most powerful diesel auto engines BMW has developed, showcasing their robust engineering and high-performance output. If you’re on the hunt for a powerful, long-lasting engine for your BMW, these diesel engines are prime candidates.
The M51: BMW’s Early Diesel Engine
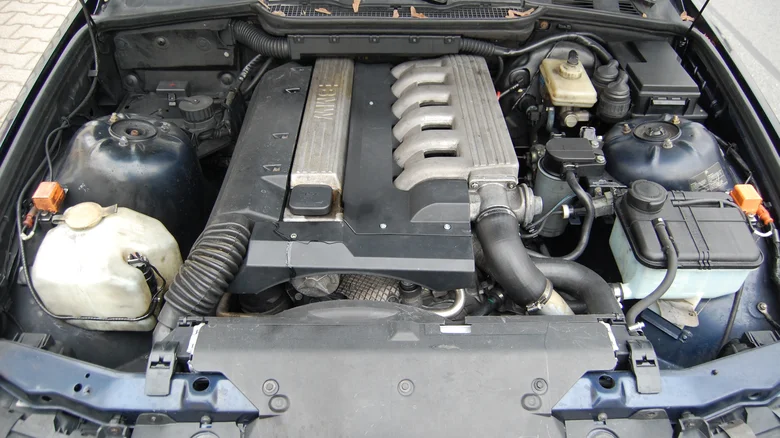
The M51 diesel engine, produced from 1991 to 2000, was a pioneering inline-six that may not have been the most powerful but was advanced for its time. It played a significant role in establishing BMW’s diesel engine lineup, powering a range of models including the 5 Series, 7 Series, and the Land Rover Range Rover 2.5 DSE during the 1990s.
This 2.5-liter engine utilized direct fuel injection, a technology that was still relatively new during the early 1990s. Some versions of the M51 were equipped with an intercooler, which increased power to 134 horsepower—close to the output of the 2007 Isuzu D-Max’s diesel engine, which had the same displacement.
The M57: A Milestone in Diesel Performance

The M57 engine replaced the M51 in the late 1990s, marking a significant leap forward in diesel technology. Known for its excellent performance and reliability, the M57 was used in various BMW cars and SUVs, starting with the 2009 BMW 335d. The M57 came in different sizes, ranging from 2.5 liters to 3.0 liters, producing between 148 and 282 horsepower and up to 428 pound-feet of torque in the twin-turbo, 3.0-liter version.
The 2009 BMW 335d, powered by the M57, became known for its impressive acceleration, going from 0-60 mph in just 5.7 seconds, and completing the quarter-mile in the low 14-second range. With aftermarket modifications like improved software, injectors, and turbochargers, M57-equipped cars can push more than 700 horsepower, all while retaining their durable stock components.
The M67: BMW’s V8 Diesel Powerhouse

The M67 series marked BMW’s entry into high-performance V8 diesel engines, produced from the late 1990s to the mid-2000s. The engine came in several versions, with displacements ranging from 3.9 to 4.4 liters, and was used in the 7 Series. The most powerful M67 variant, the D44, generated 329 horsepower and a hefty 552 pound-feet of torque.
The 745d, equipped with the M67 engine, was capable of reaching 0-60 mph in 5.8 seconds, despite weighing nearly 4,500 pounds. Its top speed was limited to 155 mph, while offering fuel efficiency of 18.4 mpg in the city and 34.6 mpg on the highway.
The M550d: BMW’s Groundbreaking Quad-Turbo Diesel

The M550d xDrive is a standout in BMW’s diesel lineup. Produced from 2017 to 2020, the G30 model of this sedan featured a 3.0-liter inline-six diesel engine with four turbochargers, delivering 400 horsepower and 561 pound-feet of torque. This setup allowed the M550d to accelerate from 0-60 mph in just 4.4 seconds, placing it among the fastest diesel-powered vehicles ever made.
The four turbochargers weren’t just for show—they helped eliminate turbo lag, providing smooth and consistent power throughout the rev range. Two smaller turbos managed low-end power, while the larger pair took over at higher engine speeds, making this engine one of the most innovative and powerful six-cylinder diesels ever produced. Its fuel economy remained strong, exceeding 45 mpg on average.
The N74 V12: A Final Diesel Beast
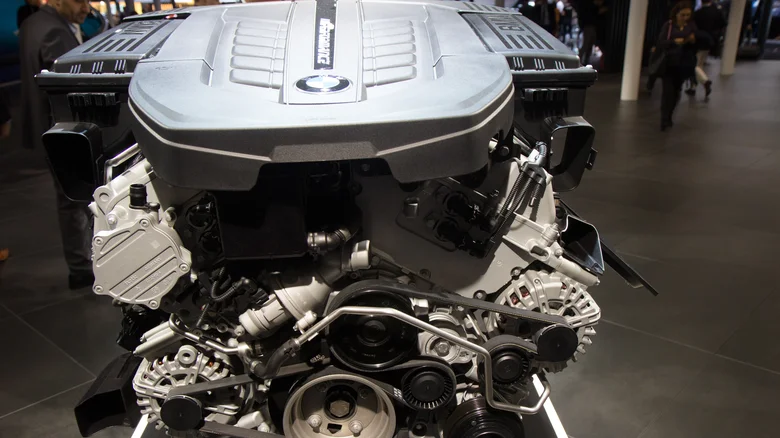
BMW’s V12 diesel engines were as powerful as they were rare, with the N74 standing out as one of the last of its kind. This engine powered select 7 Series and Rolls-Royce models, including the 2022 M760i, which was the final BMW to feature a V12 engine before the shift toward electrification.
The N74 diesel engine packed advanced features like double VANOS variable valve timing, direct injection, and twin turbochargers. This powertrain produced a massive 601 horsepower, channeled through an eight-speed automatic transmission and BMW’s xDrive system. The M760i, powered by the N74, could reach 0-60 mph in a blistering 3.6 seconds, a performance that rivaled many supercars.